The English doctor-philosopher and literary figure Thomas Browne (1605-1682) held a unique understanding and view of the world which is rewarding to explore through the perspective of geography.
Its in Religio Medici or ‘The Religion of a Doctor’ (1643) that Thomas Browne describes himself as a microcosm or little world, as well as informing his reader that he possessed a globe.
‘the world that I regard is myself. It is the microcosm of my own frame that I cast my eye upon. For the other I use it but like my globe and turn it round sometimes for my recreation. Men that look upon my outside, perusing only my condition and fortunes do err in my altitude. For I am above Atlas his shoulders’. [1]
By saying he is 'above Atlas' Browne implies that as a microcosm or little world he has transcended the burden of carrying the weight of the world on his shoulders.
The large-scale sculpture known as the Farnese Atlas (header photo) dating from the second century of the Common Era depicts the fate of Atlas. In Greek myth, the giant is condemned by the gods to hold a globe—sometimes celestial, sometimes terrestrial—on his shoulders for eternity.
During Browne’s era globes were sold in pairs: one showing the earth, the other of the heavens. The mapping of the night sky was far more detailed and accurate than the rough depictions of remote and little-known regions of Earth.
The ancient Greek Strabo (64 or 63 BC – c. 24 AD) was the author of a vast work on geography. Written during the early Roman Empire, Strabo's encyclopaedic work consists of political, economic, social, cultural, and geographic descriptions. Its the only surviving ancient text to describe the entire inhabited world known to the Roman world. In Strabo's map of the world the British Isles can be seen. (above) [2]
Also listed as once in Browne’s library is Gerard Mercator’s epic world map of 1569. (below) [3] Mercator's projection laid out the globe as a flattened version of a cylinder. His map, with its Mercator projection, was designed to help sailors navigate around the globe using its longitude meridian lines to plot a straight route. It was Dutch map-making and cartography which was crucial for Dutch explorers.
Following Dutch independence from Spanish rule in 1588 the newly formed Dutch Republic grew prosperous and expanded with overseas territory, notably in the East Indies. The Northern European port of Amsterdam became one of Europe’s busiest trading centres and superseded Venice as an importing and exporting port in the 17th century. Just as during the Middle Ages the sea port of Venice was a major European trading centre with its network of canals used to convey and store imported goods to merchant’s storehouses from the Near East, so too Amsterdam with its man-made network of canals became the predominant sea and trading port in the 17th century.
The 16th/ 17th centuries were an era of great exploration and discovery, notably through adventurers such as Olivier van Noort the first Dutchman to circumnavigate the world - Willem Schouten the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean , Cornelis de Houtman, who explored the East Indies - Willem Janszoon the first European to see the coast of Australia in 1606 and Cornelis Nay, explorer of the Arctic - The most notable Dutch explorer of the 17th century was Abel Tasman the first European to discover New Zealand and Fiji. The Dutch also made important contributions to horticulture, land reclamation, and art throughout the 17th century.
Dutch engraver Pieter van den Keere’s 12 sheet map of 1611 (above) was wall mounted. Its border shows 14 cities and the rulers of seven nations. Stylized pairs of figures in the national costume of national cultures are also depicted on it.
Its often said that the 16th/17th centuries were advanced through three driving inventions- Printing , the Mariner’s Compass and Gunpowder, each of which transformed the lives of many in this era.
Thomas Browne’s life spanned not only the Dutch 'Golden Age' but also England’s most traumatic century. He was born just weeks before the Gunpowder Plot of 1605 and lived through the events of the English Civil war, the execution of King Charles, the Commonwealth of Cromwell, the subsequent Restoration of Monarchy, the Great plague of 1665 and the Fire of London in 1666.
From his residence for an academic year in Montpellier in France, Padua in Italy and Leyden in Holland Browne acquired a privileged education and an appreciation of other cultures. His celebrated tolerance adhered to the maxim of ‘when in Rome do as the Romans’ as regards cuisine and food, as he frankly tells his reader -
‘I wonder not at the French for their dishes of frogs and toadstools, nor at the Jew for locusts and grasshoppers but being amongst them make them my common viands. And I find they agree with my stomach as well as theirs.’ [4]
Of greater importance Browne also recognised a major cause of hatred, one which remains so to the present day, that of nationalism. Nationalism, if zealous, encourages those who, purely from an accident of birth to consider their own nation to be the World’s best, and to dislike or even hate other Nationalities, often without having ever visited or even met anyone from the country which they hate. Browne’s continental education inoculated him against this prejudice, as he informs us-
‘I find not in me those common antipathies I discover in others. Those national repugnances do not touch me, nor do I behold with prejudice, the French, Italian, Spaniard or Dutch. But where I find their actions in balance with my countrymen, I honour love and embrace them to the same degree. All places, all airs are unto me one country, I am in England everywhere under any meridian’. [5]
Browne was able to give full expression to his interest in world geography, culture and customs in his subsequent work, the groundbreaking Pseudodoxia Epidemica which was first published in 1646. Its Latin title might loosely be translated as 'Pandemic of fake news'. Pseudodoxia is a pioneering work and firmly in the vanguard of the early Scientific Revolution. Consisting in total of over 200,000 words, its sixth book addresses queries historical and geographical. He points out that the terms East and West are dependent on where exactly one is located in the world and informs his reader on the botany and zoology of America. He also reveals an uncommon knowledge of cartography in discourse on the number of mouths of the Egyptian river Nile -
'Ptolomy an Egyptian, and born at the Pelusian mouth of Nile, in his Geography maketh nine: and in the third Map of Africa, hath unto their mouths prefixed their several names; ..... wherein notwithstanding there are no less then three different names from those delivered by Pliny. ....Lastly, Whatever was or is their number, the contrivers of Cards and Maps afford us no assurance or constant description therein. For whereas Ptolomy hath set forth nine, Hondius in his Map of Africa, makes but eight, and in that of Europe ten. Ortelius in the Map of the Turkish Empire, setteth down eight, in that of Egypt eleven; and Maginus in his Map of that Country hath observed the same number. And if we enquire farther, we shall find the same diversity and discord in divers others'. [6]
Other prejudices which persist to this day are also tackled in Pseudodoxia - why do some people differ in the colour of their skin, why does the skin-pigmentation of American natives differ from African natives, as well as the thorny question- why does the religious prejudice of antisemitism persist ? He also recognised that what is considered to be beautiful in facial appearance and body decoration differs enormously between world cultures, stating-
'Thus flat noses seem comely unto the Moore, an Aquiline or hawked one unto the Persian, a large and prominent nose unto the Romane; but none of all these are acceptable in our opinion. Thus some think it most ornamentall to wear their Bracelets on their Wrests, others say it is better to have them about their Ancles; some think it most comely to wear their Rings and Jewels in the Ear, others will have them about their Privities; a third will not think they are compleat except they hang them in their lips, cheeks or noses'. [7]
One of the best gateways to understanding of a different culture is through learning its language. The Reverend Whitefoot, who was Browne’s lifelong friend, informs us that his friend was familiar with all the languages printed in Hutter’s polyglot New Testament of 1599. Hutter’s New Testament (above) includes the languages of Syrian, Hebrew, Greek, Latin, German, Bohemian, Italian, Spanish, French, English, Danish and Polish. These 12 languages are printed in side-by-side-columns of 3 languages per page. Hutter’s polyglot Bible encouraged Christians to read and study the Hebrew language. Browne’s own interest in Hebrew was instrumental in his study of the esoteric lore of the Kabbalah. [8]
With his deep interest in languages Browne was well-equipped to introduce badly needed new words, often of a scientific nature into English language. Although its not quite a foreign language he also took an interest in the peculiarities of the Norfolk dialect and noted these words to be in common use in Norfolk such as Bunny, Mawther, Kedge, Seele, Straft, Matchly, Dere, Nicked, Gadwhacking Stingy, Sap, Cothish, Thokish, and Paxwax. Strong traces of the Dutch tongue can be heard in Norfolk dialect to the present day.
Paris syndrome has been described as a severe form of culture shock and a sense of extreme disappointment experienced by only a handful per million when visiting Paris and is believed to be caused by factors such as language barrier, cultural differences, exhaustion and above all else, idealization.
With his deep interest in unusual psychic phenomena and introduction of the words 'pathology' and 'hallucination' into the English language, Thomas Browne was well qualified to identify the phenomena of Paris syndrome. Within the following paragraph he names ten geographic locations, defines the ozone-rich air of East Anglia as 'Aerial Nitre', introduces the word 'migrant' into English and advises against 'infirm heads' that is, impressionable minds from visiting Venice or Paris.
‘He was fruitlessly put in hope of advantage by change of Air, and imbibing the pure Aerial Nitre of these Parts; …..He is happily seated who lives in Places whose Air, Earth, and Water, promote not the Infirmities of his weaker Parts, …..He that is weak-legg'd must not be in Love with Rome, nor an infirm Head with Venice or Paris. Death hath not only particular Stars in Heaven, but malevolent Places on Earth,…..in which Concern, passager and migrant Birds have the great Advantages; who are naturally constituted for distant Habitations, whom no Seas nor Places limit, but in their appointed Seasons will visit us from Greenland and Mount Atlas, and as some think, even from the Antipodes. [9]
Browne’s speculation on the migration routes of birds is a reminder of his keen interest in feathered creatures. At one time of another he kept an owl, a cormorant, a kestrel and an eagle. He's also credited with introducing the word 'incubation' into English. It was in his lifetime that one of the first recorded extinctions of a species of bird occurred.
The first recorded mention of the flightless bird known as the dodo was in 1598 by Dutch sailors when they discovered Mauritius, a small island near Madagascar which was a useful stopping-off point for Dutch sailors en route to the East Indies. Because the Dodo is a flightless it was easily captured by hungry sailors. Browne’s contemporary the Royalist politician, Sir Hamon L’Estrange of Hunstanton in Norfolk wrote of a dodo he saw exhibited in London in 1638.
‘About 1638, as I walked London streets, I saw the picture of a strange fowl hung out upon a cloth canvas, and myself, with one or two more then in company, went in to see it. It was kept in a chamber, and was somewhat bigger than the largest turkey-cock, and so legged and footed, but stouter and thicker, and of a more erect shape, coloured before like the breast of a young cock-fesan, and on the back of a dunne or deare colour. The keeper called it a dodo; and in the end of a chimney in the chamber there lay a heap of large pebble-stones, whereof he gave it many in our sight, some as big as nutmegs; and the keeper told us she eats them (conducing to digestion); and though I remember not how far the keeper was questioned therein, yet I am confident that afterwards she cast them all again.
The last recorded sighting of a dodo was in 1662. The bird was immortalized by Lewis Carroll in his ‘Alice in Wonderland.’ The character of the dodo is believed to be inspired by a specimen of a dodo exhibited in the Oxford University Museum which Carroll frequently visited.
Exploring world cultures can be enriched through collecting artifacts from near and far, whether it's treasures gathered during travels or acquired locally. In an era long before photography, those with means could hire artists to capture the essence of these treasured possessions, preserving memories of exotic journeys and far-off lands.
Sir Robert Paston of Oxnead Hall, near Alysham commissioned an unknown Dutch artist to paint a selected fraction of his collection of art-objects, some of which were acquired when his father visited Jerusalem and Cairo. Dating from circa 1665 The Paston Treasure (above) has a Multi-layered narrative, its simultaneously, a record of the Robert Paston’s collection, a Vanitas painting and a microcosm of the world in the 17th century, as hinted by the prominent position of a globe. Browne would have seen this painting when visiting the Paston’s and given that in Religio Medici he confesses, 'I can look a whole day with delight upon a handsome picture, though it be but of an horse’ he would without doubt delighted in viewing it.
The world’s continents are represented in The Paston Treasure by - a packet of tobacco from America, a boy and parrot from Africa, and a porcelain dish from Asia. Sculptures and gems, gold, silver and enamel, as well as music instruments of a bass viol, sackbut, violin and lute can also be seen. The peaches, grapes and oranges, along with lobster, suggest a luxurious lifestyle.
The Paston Treasure also expresses a moral warning - life has sudden, unexpected disturbances - the servant is disrupted from his duties by a monkey which has jumped onto his shoulder, the young girl is interrupted from her singing by a parrot alighting on the music she’s reading.. In recent years The Paston Treasure has been restored, exhibited in America and studied in depth by the art-historian Spike Bucklow in his excellent, insightful book. Today, it can be seen in Norwich Castle Museum.
One unique feature of Browne’s prose is his usage of geographical places and historical persons as symbols. For example he describes the difficulties in his compiling an encyclopaedia, as, 'oft-times fain to wander in the America and untravelled parts of truth'. Geographical place name symbols along with historical persons symbols can be found in Browne’s philosophical work, the two-in-one diptych discourses of 1658, Urn-Burial and The Garden of Cyrus.
These two 17th century images, the Nigredo stage of the alchemical operation (left) and 'The Garden of Mathematical Delights'( right) both from books once in Browne's library, are I believe, excellent visual representations of the thematic concerns and mood music of each respective discourse. (Click on picture to enlarge).
The melancholic, Grave and Saturnine meditations upon human suffering in Urn-Burial are ‘answered’ by the Mercurial Garden delights of Cyrus. A multiplicity of opposition or polarities occur in Browne’s literary diptych, in their respective themes, imagery, truth and literary style. Urn-Burial opens 'in the deep discovery of the subterranean world' and concerns itself with the oblivion of Time, in complete contrast The Garden of Cyrus concerns itself with Space and opens with ‘shooting rays and diffused light’ of the Creation before continuing in speculation on the geographical location of the Garden of Eden. [11]
In Browne’s geographical symbolism America invariably symbolizes the new, the unknown and exotic. In contrast the proper place name of Persia is used as a symbol of magic and esoteric wisdom. These two geographical symbols are juxtaposed in a startling way at the conclusion of The Garden of Cyrus - in doing Browne highlights how Humankind’s collective consciousness ebbs and flows between those who are waking up and conscious while others fall asleep and are unconscious.
‘The huntsmen are up in America and they are already past their first sleep in Persia'.
But perhaps the most famous example of Browne’s geographical symbolism occurs in Religio Medici, where he inspirationally declares – ‘We carry within us, the wonders we seek without us.There is all Africa and her prodigies in us’. [12]
The psychologist Carl Jung when hearing this quote while visiting Kenya, East Africa, was impressed and immediately made note of it. Actually there’s a fascinating relationship between the famous Swiss psychologist Jung to Browne, both were doctors interested in the interpretation of dreams, both read esoteric authors and both were interested in the geography of the mind, and mapping of the psyche’s contents. [13]
Together, Urn-Burial and The Garden of Cyrus are Browne’s great work of psychology. Historical personages are employed by him as symbols in order to illustrate archetypes, that is, the first, original forms of the psyche as envisioned by Plato and Hermetic philosophers. Browne’s proto-psychology attempts in Cyrus to delineate the archetype of the wise ruler through historical name symbolism, mentioning Moses, Solomon, Abraham, Alexandria the Great and the titular Cyrus as exemplars of the wise ruler. Women aren’t overlooked in his proto-psychology, the archetype of the 'Great Mother' is sketched through inclusion of the nurturing Old Testament matriarch Sarah, the Roman goddess Juno and the Egyptian goddess Isis.
* * *
With the colonization of South America by the Spanish and Portuguese in the seventeenth century, as well as European migration to North America, along with the opening of trading routes to the East Indies and China, an abundance of published reports upon exotic flora and fauna became available to the physician. Tobacco and the potato were early exports from America to Europe throughout the 17th century.
It was the Swiss alchemist-physician Paracelsus (above) who encouraged his fellow physicians to experiment with substances from the vegetable, mineral and animal kingdoms in order to discover new medicines and new cures. We can be confident that Doctor Browne of Norwich was a committed follower of Paracelsus (1493-1541), not only are the 'Luther of Medicine''s bulky writings listed as once in his vast library but the very word used by Paracelsus to describe his distinctive kind of medical alchemy, known as spa-gyric ( meaning to separate and conjoin) can be seen inscribed upon Browne's coffin-plate, one half of which survives on display at Saint Peter Mancroft. The distinguished Canadian physician Sir William Osler (1849-1919) who was a great admirer of Browne commissioned a replica of this brass Coffin-plate. It can be seen at the Norfolk and Norwich Sir Thomas Browne Medical Library. [14]
A great example of Browne’s following Paracelsian medicine occurs in his assessment of so-called Peruvian Bark, the source of the drug known today as Quinine.
A Jesuit priest is credited as among the first to observe that the Inca people use a diffusion of the bark from the cinchona tree to ease the symptoms of malaria. Indeed the original Inca word for the cinchona tree bark, 'quina' or 'quina-quina' which roughly translates as 'bark of bark' or 'holy bark'. In 1638, the wife of a Peruvian viceroy used the bark to relieve her fever-induced symptoms during the onset of malaria. Her remedy was called a 'miracle cure'. By 1658 an English newspaper advertised - 'The excellent powder known by the name of 'Jesuits' powder' may be obtained from several London chemists'.
Although Peruvian Bark was hailed as a successful medicine for malaria due to religious prejudice it was not officially recognised in England until 1677. Because it was known as 'Jesuits' Powder' it was tainted with associated with Catholicism. Even among the educated such as King Charles the Second, who took an active interest in the new scientific enquiry advanced by the Royal Society, was suspicious of 'Jesuit's Powder' because of its presumed association with Catholicism. However when the King suffered from a malarial fever he consulted a Mr Robert Talbor who was obliged to give the King the bitter bark decoction in great secrecy. The treatment completely relieved King Charles from malarial fever and he rewarded Talbor handsomely with a lifetimes membership of the newly-formed Royal Society.
Several 17th century English physicians were interested in reports of the healing qualities of Peruvian Bark, especially those who lived in regions prone to the spread of malaria; East Anglia with its marshes, broads, large tracts of low-laying land and slow-flowing, stagnant stretches of water was an ideal habitat for the spread of the insect-borne virus.
In correspondence to his youngest son nicknamed ‘Honest Tom’ Browne requested of him -
'When you are at Cales, see if you can get a box of the Jesuits' powder at easier rate, and bring it in the bark, not in powder'. [15]
Browne’s request to obtain Jesuits' powder from a Continental source and not from London suggests he knew that the thriving trade in Peruvian Bark was vulnerable to dilution by apothecaries. His insistence on bark and not powder also suggests he was familiar with Peruvian Bark's composition. His assessment of Peruvian bark in an undated letter is considered one of the most detailed in British medical history-
Another new substance introduced to Europe, in this case through trade with China, was the root known as Ginseng.
Because the shape of the fleshy Ginseng root resembles the torso and limbs of a human, all kinds of medical and healing properties have been attributed to it. Widely cultivated in China for centuries Ginseng is used in Chinese medicine as a muscle relaxant. In correspondence to his eldest son Edward, Dr. Browne wrote-
Deare Sonne, - You did well to observe Ginseng. All exotick rarities, especially of the east, the East India trade having encreased, are brought in England, and the profitt made therof. Of this plant Kircherus writeth in his China illustrata. [16]
Today ginseng is scientifically recognised for its anti-carcinogenic and antioxidant properties
Throughout the 1650s and 1660s England found itself embroiled in conflict with the newly-emerging economic power and global trade of the Dutch Republic. British resentment towards the newly emerging European power is perceptively articulated by the art-historian Simon Schama, who noted of Johan De Witt, the chief negotiator for the peace treaty of the Second Anglo-Dutch War -
‘British enmity, on the other hand, he knew to be chronic and rooted in the very nature of the Republic’s existence, or at least its prosperity. The problem, he supposed in common with many of his compatriots, was that, in matters of trade, the British were poor losers. Unable to match the Dutch in resourcefulness, industry, or technical ingenuity, they were prepared to bludgeon their way to wealth by the assertion of deliberately bellicose principles and by interfering with the freedom of trade. Peevish envy had turned them into a gang of unscrupulous ruffians who would stop at nothing to burglarize the Dutch warehouse, pretending all the time that some cherished issue of sovereignty had been infringed. [17]
One of Browne’s greatest personal tragedies was hearing from the British Admiralty that his son Midshipman Thomas, ‘Honest Tom’ had been lost in action and presumed dead aged 21.
A solitary piece by Browne, written for the entertainment of young Midshipman Tom survives. 'The Sea-battle’ is a vivid narration of an ancient world Sea-battle. Written in Latin its conclusion is a valuable insight on a primary cause of war.
'The cause of this war was that of all wars, excess of prosperity. As wealth arises spirits rise, and lust and greed of power appear; thence men lose theiir sense of moderation, look with distaste on the prosperity of others, revolve disquiet in their mind, and throw overall settlement, for fear lest their enemies’ wealth be firmly established, they put their own to risk; and finally (as happens in human affairs) fall into slavery when they seek to impose it, and earnestly courting good fortune, experience disaster.' [18]
In his old age Browne seems to have taken an even greater interest in traveller’s accounts of exotic locations and newly discovered lands. Its testimony to his eldest daughter Elizabeth’s education, patience and devotion that her father recorded the following in his Commonplace notebooks –
‘Books which my daughter Elizabeth hath read unto me at nights till she read them all out -All the Turkish historie - All the history of China - All the travels of Olerarius and Mandelslo -All the travels of Taverniere - All the Travels of Petrus della valle - All the travels of Vincent Le Blanc -All Sandys his travels - All the travels of Pinto - All the travels of Gage - -All the history of Naples -All the history of Venice - Some hundreds of sermons. Many other Books, Treatises, discourses of several kinds. [19]
But perhaps the traveller Dr. Browne took the greatest interest in was his eldest son, Edward Browne (1644-1708). In 1668 Edward made a tour of Holland and Germany visiting museums, libraries, and churches. When later based in Vienna he made three long journeys, one to the mines of Hungary, one to Thessaly, another into Styria and Carinthia. Wherever Edward Browne travelled he acted as the dutiful eyes and ears of his father, who instructed him with advice such as-
'Take notice of the various Animals, of places, beasts, fowles, & fishes; what the Danube affordeth, what depth, if conveniency offers, of mines, minerall works, Beside naturall things you may enquire into politicall & the government & state & subsistence of citties, townes & countries… observe how the Dutch make defences agaynst sea inundations…' [20]
Also included among the travel books in Browne’s vast library is Thomas Fuller’s guide to the sights and places of the holy land of Palestine. Fuller's book A Pis-pah Sight was important in its day and includes a detailed account of the geography and history of Palestine. Incidentally, it was Thomas Fuller in his Worthies of England who described the Norwich of Browne's day to be, 'either a city in an orchard, or an orchard in a city, so equal are houses and trees blended in it'. [21]
Another noteworthy geography book once in Browne’s library is Athanasius Kircher’s China Illustrata. Dating from 1665 China illustrata was printed in Amsterdam. A work of encyclopaedic breadth, it included accurate maps as well as mythical creatures. It drew heavily on reports by Jesuit missionaries who worked in China. Kircher’s book remained the most informative source on China for over two centuries. [22]
In the above illustration Chinese botany and horticulture, costume and customs, along with architecture, are all faithfully recorded from an eyewitness account of a social gathering, a feast upon giant jackfruit.
It may well have been while turning his globe round sometime for his recreation that Browne was inspi to pen his ‘Prophecy concerning the future State of Several Nations’ . It was written after the Pandemic of Bubonic plague and the Great Fire of London in 1666 in which an estimated one hundred thousand people perished, some twenty percent of London’s entire population perished. In all probability it was inspired after he was shown a copy of the French doctor Nostradamus’s prophecies, the first translation English into English in 1672.
In his doggerel verse and parody of Nostradamus’s barely intelligible prophecies Browne makes some astounding predictions, which are based upon nothing more than the solid combination of rational conjecture and a deep knowledge of geography and history. In one of its seven rhyming couplets Browne questions the morality of the growing Slave-trade, long before its eventual abolition –
'When Africa shall no longer sell out its Blacks/to be Slaves and drudges to the American Tracts'.
At a time when it was only a fledgling colony, Browne predicted that one day America would become Europe’s economic equal -
'When the New World shall the old invade/ nor count them their Lords but their Fellows in Trade'.
Remarkably, he also 'predicted’ that America would one day become a Nation which pursued happiness and engage in economic protectionism.
'When America shall cease to send out its treasure/but employ it instead in American Pleasure’. [23]
Browne's miscellaneous tract known as Museum Clausum his solitary work of fiction, an inventory of lost, rumoured and imaginary books, pictures and objects, also includes geographical speculations. In the 16th century, the voyage of Hanno saw increased scholarly interest in an age when European exploration and navigation were flourishing. Already then, the extent of Hanno's voyage was debated. Browne makes mention of the explorer Hanno in Museum Clausum thus -
'A learned Comment upon the Periplus of Hanno the Carthaginian, or his Navigation upon the Western Coast of Africa, with the several places he landed at; what Colonies he settled, what Ships were scattered from his Fleet near the Equinoctial Line, which were not afterward heard of, and which probably fell into the Trade Winds, and were carried over into the Coast of America'. [24]
In all probability its through his friendship with the Icelandic Lutheran minister Theodor Johannsson that Browne also includes in Museum Clausum -
'A Snow Piece, of Land and Trees covered with Snow and Ice, and Mountains of Ice floating in the Sea, with Bears, Seals, Foxes, and variety of rare Fowls upon them'. [25]
Browne’s view of the world's future was one which was, ‘not like to envy those that shall live in the next, much less three or four hundred Years hence, when no Man can comfortably imagine what Face this World will carry: [26]
He was aware of several disastrous scenarios which threaten life on Earth and knew that an increase in global traffic has medical implications, stating in A Letter to a Friend- ‘New Discoveries of the Earth discover new Diseases'. He knew of the threat of asteroids from outer Space impacting Earth, and wrote of ‘a mighty stone falling from the clouds which antiquity could believe Anaxagoras was able to foretell half a year before’. [27] And also made the sombre cosmological observation that - 'The created world is but a small parenthesis in Eternity.’ [28]
Before revealing what is arguably one of Browne’s greatest linguistic contributions to our modern age, its worthwhile remembering that while today he’s often promoted for his scientific profile, Browne’s worldview in essence was a synthesis of a deeply held Christian faith, adherence to hermetic philosophy and scientific empirical enquiry. There’s far greater value in reading Browne today for his moral, psychological, and spiritual insights than his 'occular observation' of the natural world. As a doctor, it’s the geography of the mind which interests him most. He would with little doubt whole-heartedly agreed with Carl Jung’s assertion that- ‘Science and technology have indeed conquered the world, but whether the psyche has gained anything is another matter'. [29]
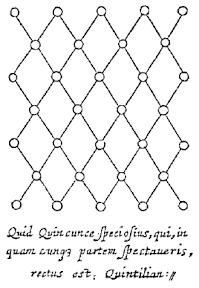
The Garden of Cyrus (1658) has a frontispiece ‘borrowed’ from a book by one of Browne's favourite authors, the Italian polymath Giambattista Della Porta (1535-1615). Its Latin quotation reads, ‘What is more beautiful than the Quincunx, which, no matter how you view it, present straight lines’.
The full running title of The Garden of Cyrus includes what is one of Browne’s greatest neologisms, one which is highly relevant to our modern age, that of ‘Network.’ He probably encountered the word ‘network’ from reading of the Bible where its used to describe the decorative and structural design of Solomon’s temple. What is certain is that Browne was the first to write about net-like or reticulated structures in subjects as diverse as art, architecture, metalwork, botany, marine life and anatomy, in order to illustrate his concept. It’s a word which underscores his hermetic belief in the interconnectivity of all life-forms in the world. In the 19th century usage of the word ‘network’ gathered steam after the new railway routes of England were described as a network. Today in our increasingly inter-connected world the word ‘Network’, with its strong geographical associations, has expanded to include social, transport, communication and technological meanings.
Here in Norwich today we can take pride in the fact that it was once the home of a polymath mind who observed and wrote of Networks, introducing it, among many others into English language. The word Network is exemplary, not only of Sir Thomas Browne’s contribution to scientific vocabulary but also his mystical ‘Above Atlas’ worldview.
.jpg)










.jpg)








_engraving_from_China_monuments_-_(MeisterDrucke-1464576).jpg)